Note: A new Climate Warehouse website is under development. This page provides an overview of the World Bank’s ongoing initiatives to enhance transparency, trust, and interoperability in carbon markets.
About the Climate Warehouse Program
The Climate Warehouse program, under the innovation pillar of the Partnership for Market Implementation Facility (PMIF), catalyzes solutions that strengthen the enabling environment for carbon markets, pilots new approaches to foster high-integrity crediting, and lays the foundation for scalable and connected markets. Through this work, it advances innovation and readiness for the next generation of carbon market mechanisms.
The program has four complementary work streams as shown in the chart below:
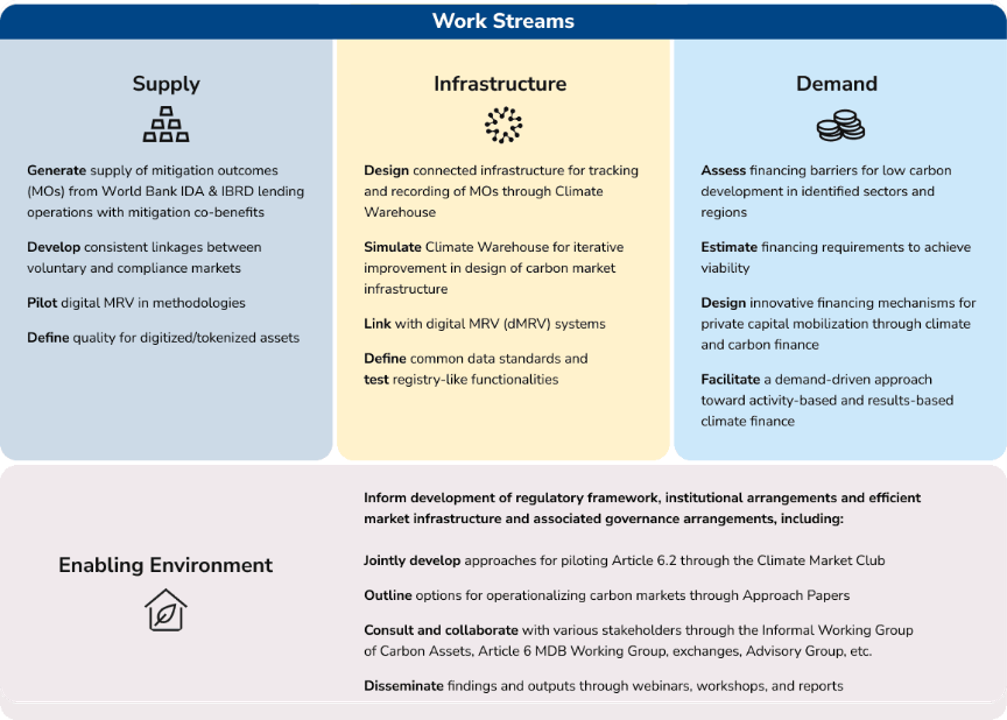

Our Initiatives
Climate Warehouse
The Climate Warehouse initiative supports the development of digital infrastructure to strengthen the transparency and integrity of carbon markets. By connecting registries, promoting common data standards, and fostering collaboration across the value chain, Climate Warehouse helps lay the foundation for a high-integrity, interoperable global carbon market.
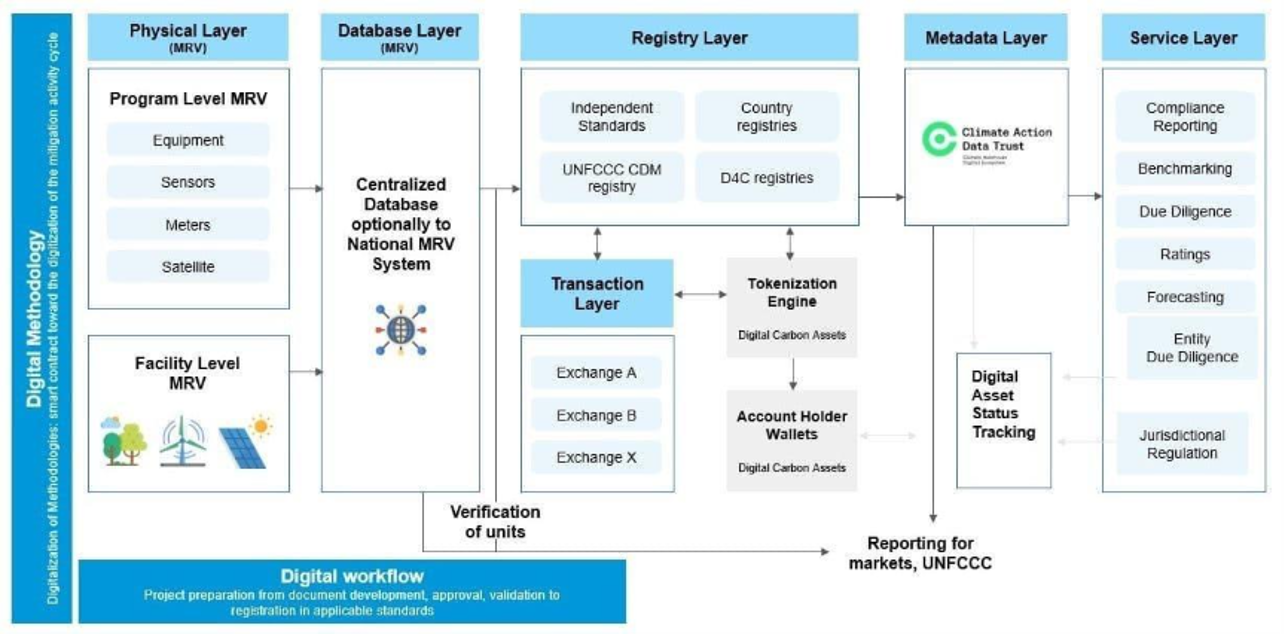
Building the Digital Infrastructure for Carbon Markets
Climate Warehouse is designing, prototyping, and testing the digital building blocks that will enable secure and connected carbon markets. Successful components are now being scaled and deployed, including:
- a metadata layer (now the independent Climate Action Data Trust),
- digital MRV systems,
- open-source national carbon registries,
- tools to issue and track digital carbon assets (native and permissioned tokens), and
Together, these elements form a trusted, efficient, and interoperable digital ecosystem for carbon markets.
End-to-End Digital Ecosystem for Carbon Markets
Carbon Market Infrastructure (CMI) Working Group
The Carbon Market Infrastructure Working Group (CMI WG), convened by the World Bank as a follow-up to the Engagement Roadmap for Carbon Markets, brings together policymakers, regulators, exchanges, standard setters, and infrastructure providers to strengthen the foundations of global carbon market infrastructure.
The group includes over 45 organizations working to improve interoperability, efficiency, and integrity across the carbon market ecosystem. Through five Technical Guidance Notes, it has provided practical tools and recommendations on ecosystem governance, transaction integrity, information security, data interoperability, and digital MRV—helping to build trust, scalability, and transparency across carbon market systems.
The five technical guidance notes developed by the CMI WG can be found here.
Climate Market Club
As of June 2025, the Club comprises 16 governments and five non-sovereign entities. The World Bank Group, in coordination with other multilateral development banks (MDBs), serves as the Secretariat, convening meetings and developing technical and knowledge products at the request of members.
The Club serves as a forum for dialogue and consensus-building on how key elements of Article 6.2 can be tested and refined through practical experience. This work supports the development of operational guidance under the Paris Agreement and helps catalyze early cooperative action.
Current members include:
Governments: Bangladesh, Bhutan, Chile, Ghana, Kazakhstan, Japan, Peru, Rwanda, Senegal, Singapore, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine, Namibia, Nigeria, and Thailand.
Non-sovereign entities: KliK Foundation, Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI), Temasek, Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES), and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
Mitigation Action Assessment Protocols (MAAP and MAAP-ITR)
The Mitigation Action Assessment Protocol (MAAP) provides a framework to evaluate the quality and integrity of mitigation activities across carbon markets. Developed by the World Bank and partners, MAAP assesses environmental integrity, governance, and sustainable development contributions, reinforcing confidence in climate results.
The MAAP for International Transfer Readiness (MAAP-ITR) helps countries assess their readiness to participate in international carbon markets. It identifies institutional, technical, and capacity gaps and facilitates dialogue between governments and development partners to strengthen market infrastructure and governance systems.
Approach and Structure
MAAP-ITR follows a step-by-step approach to help countries plan their participation in carbon markets. It begins with a high-level analysis of sectoral emissions, NDC targets, and proposed mitigation actions to identify where market opportunities lie—helping governments and partners understand which sectors are most suitable for voluntary carbon markets, the Article 6.4 mechanism, or Article 6.2 cooperative approaches.
Building on this foundation, MAAP-ITR provides a structured readiness assessment through four core modules, reflecting common policy and institutional frameworks:
- Governance and Institutional Arrangements – defining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes.
- Authorization and Participation Frameworks – establishing rules and procedures for approving and managing carbon market activities.
- Accounting, Tracking, and Transparency – ensuring robust reporting and preventing double counting.
- Environmental and Social Integrity – aligning activities with NDCs and ensuring high-quality, sustainable outcomes.
Each module includes key indicators based on international ‘best practice’, allowing countries to choose between a simplified assessment (for early-stage readiness) or a detailed assessment (for more advanced systems).
Background and Use
The MAAP-ITR was first developed in 2018 as part of the World Bank’s broader Mitigation Action Assessment Protocol to help countries prepare for participation in Article 6 cooperative approaches. Since then, it has been regularly updated to reflect new guidance from the Paris Agreement negotiations and evolving best practices. Its scope has expanded beyond Article 6.2 to also cover the Article 6.4 mechanism and voluntary carbon markets, providing a comprehensive framework for assessing readiness.
The tool has been applied in multiple countries worldwide, with several governments using it repeatedly to track their progress. This iterative use helps countries measure improvements in institutional frameworks and market infrastructure, while also enabling sovereign buyers and development partners to monitor evolving capacity-building and technical assistance needs.
To access the tool, please email: pmiclimate [at] worldbank.org (pmiclimate[at]worldbank[dot]org)
Multilateral Development Bank (MDB) Working Group
The MDB Working Group on Carbon Markets coordinates multilateral development banks’ efforts to align technical assistance, tools, and knowledge sharing for countries engaging in carbon markets. Through collaboration and harmonized support, the group helps countries implement Article 6 and advance the global carbon market agenda.
The MDB WG’s goal is to position Article 6 as a high strategic priority in climate negotiations and encourage Parties to leverage cooperative approaches under Article 6 as an important tool to deliver Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) commitments cost-effectively. A second objective is to find mutually interesting opportunities to pilot Article 6 transactions through the MDB investment portfolio.
The MDB WG serves as the Secretariat of the Climate Market Club, supporting the development of modalities for piloting activities under Article 6, paragraph 2 of the Paris Agreement. Also, the WG participates in public consultations as a consultative group to share their insights on potential governance, carbon credit and market integrity principles that would sustain the operation of the next generation of the carbon market.
Knowledge Base
Note: Please display the relevant knowledge products tagged as Climate Warehouse or Carbon Market Infrastructure.

